A herniated disc results from a torn outer layer allowing the inner material to press on nerves, causing pain, numbness, and weakness. Common causes are aging and injuries, with treatment ranging from conservative (rest, exercises, physical therapy) to intensive (functional rehabilitation). Many prefer natural healing methods, and conservative treatments can facilitate self-healing. Persistent symptoms may require specialized functional rehab to address root causes and prevent future injuries.
“Discovering the path to healing with a herniated disc doesn’t always require intense intervention. Often, these discs can heal on their own through conservative treatments. This comprehensive guide explores the causes and symptoms of herniated discs, delving into effective conservative options that may alleviate pain and promote self-healing. Learn when intensive care is necessary and gain insights into navigating your recovery journey. Explore various herniated disc treatment approaches tailored to your needs.”
- Understanding Herniated Discs: Causes and Symptoms
- Conservative Treatment Options for Self-Healing
- When Intensive Intervention is Necessary
Understanding Herniated Discs: Causes and Symptoms
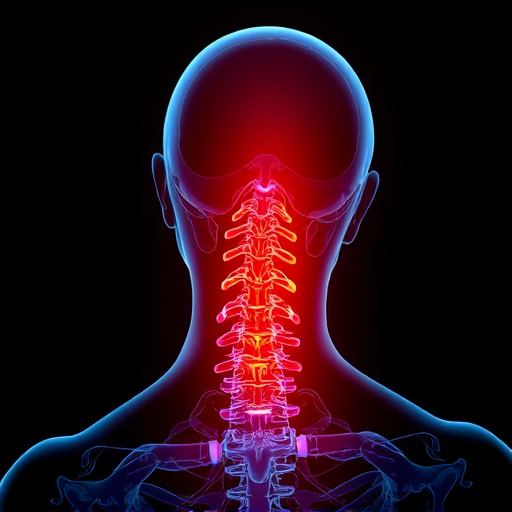
A herniated disc occurs when the soft, gel-like material inside an intervertebral disc pushes through a tear in its outer layer. These discs act as cushions between the vertebrae in your spine, providing flexibility and absorbing shock from everyday movements. When a disc becomes herniated, it can put pressure on nearby nerves, leading to a range of symptoms.
Common causes include aging, where the discs gradually lose water content and become less flexible, making them more susceptible to tears. Sudden injuries, such as those experienced in auto accidents or heavy lifting, can also lead to hernias. Symptoms vary depending on the affected area but often include sharp, shooting pain radiating to the limbs, numbness, and weakness. In some cases, chronic pain relief may be necessary to manage the condition effectively. Auto accident recovery strategies can play a crucial role in addressing herniated disc treatment, focusing on both conservative measures like rest and therapeutic exercises for faster healing.
Conservative Treatment Options for Self-Healing
Many individuals with a herniated disc wonder if it can heal on its own without intensive treatment. The good news is that in some cases, conservative treatment options can facilitate self-healing. This approach often includes rest, over-the-counter pain relievers, physical therapy, and heat or ice packs to reduce inflammation. While these methods may not directly fix the herniated disc, they can significantly alleviate symptoms and create a favorable environment for the body to heal naturally.
Soft tissue injuries, common in cases of herniated discs, often respond well to conservative treatments aimed at pain management and neck pain relief. Physical therapy plays a crucial role here, focusing on exercises that strengthen the back and core muscles, improve flexibility, and promote better posture. These techniques not only reduce pressure on the affected area but also empower individuals with long-term strategies for maintaining disc health.
When Intensive Intervention is Necessary

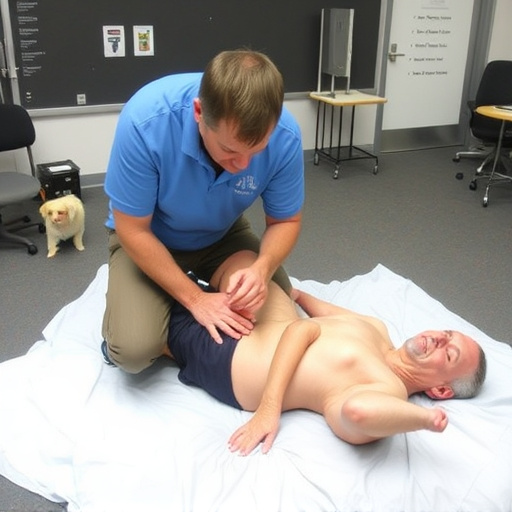
While many herniated disc cases can heal on their own with time and rest, there are instances where intensive intervention is necessary. If symptoms persist or worsen beyond a few weeks, or if there’s significant nerve compression leading to intense joint pain relief is required. In such scenarios, traditional treatments like chiropractic care might not be sufficient.
Functional rehabilitation becomes crucial in these cases. This specialized approach focuses on strengthening the back and core muscles to support the spine, improve posture, and restore range of motion. It often combines exercises, manual therapy, and patient education to address the underlying causes of the herniated disc and prevent future injuries.
While a herniated disc can be painful, it’s encouraging to know that in many cases, it may heal without intensive treatment. Conservative approaches like rest, physical therapy, and over-the-counter pain relievers can often facilitate self-healing. However, if symptoms persist or worsen, or if there are signs of nerve damage, medical intervention may be necessary. Understanding the available treatment options is key to making informed decisions about managing a herniated disc effectively.